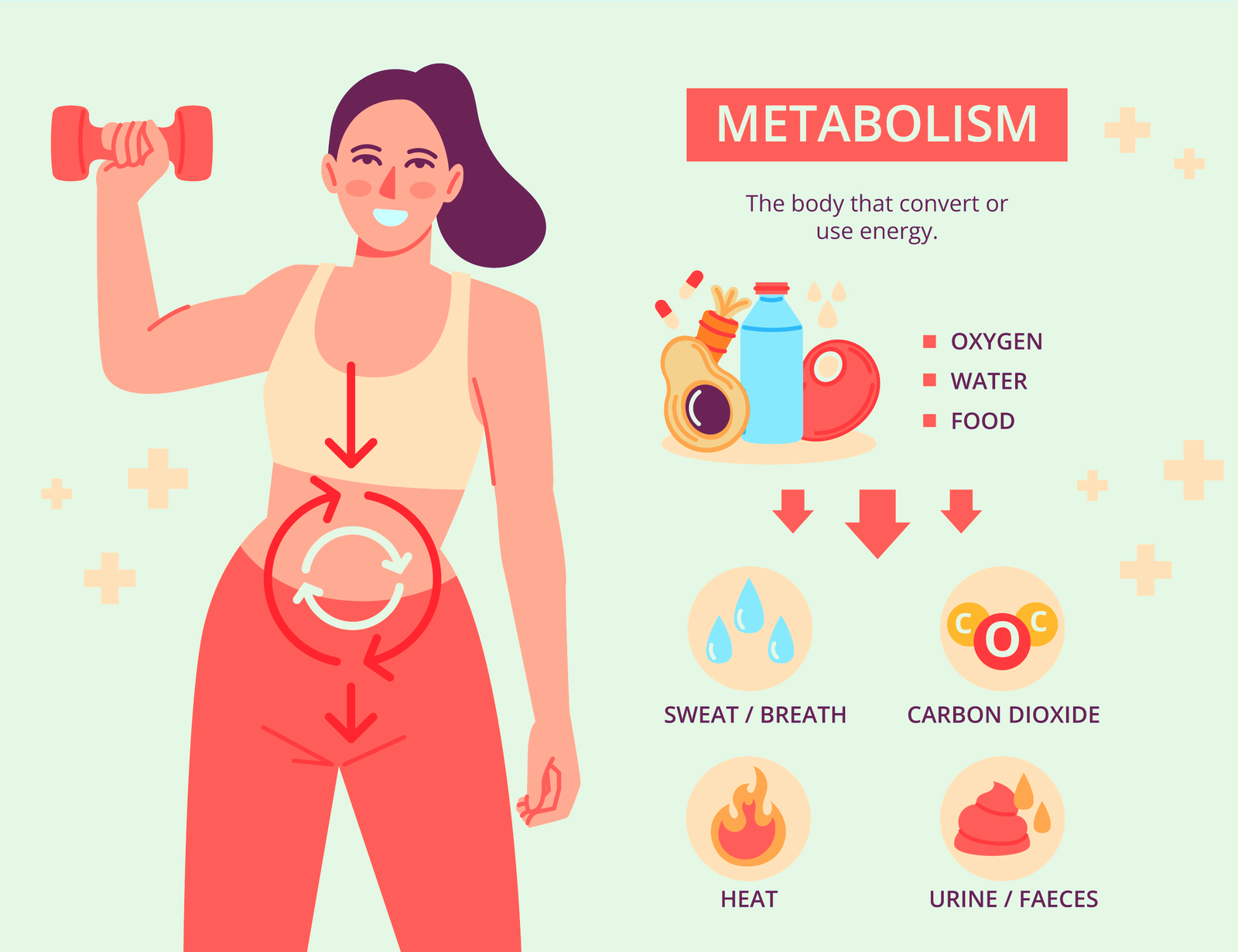
Introduction to Metabolism
An in-depth look at how and why your metabolism might be impacting your weight! (NOTE: You can jump to the bottom of the page if you’d prefer to watch a video that explain more about metabolism and how to boost it by adopting a simple daily habit!)
Metabolism is a fundamental and complex process that encompasses all the biochemical reactions occurring within the body, which convert food into energy required for daily functioning. This essential mechanism plays a vital role in maintaining physiological homeostasis, allowing the body to manage energy levels efficiently. Metabolism is often divided into two primary processes: catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism refers to the biochemical pathways that break down nutrients and organic matter, releasing energy stored in molecular bonds, while anabolism is the process of synthesizing complex molecules from simpler ones, utilizing energy to construct cellular components necessary for growth and repair.
Understanding metabolism is crucial for comprehending weight management strategies, as it significantly influences how the body gains, maintains, or loses weight. Factors such as basal metabolic rate (BMR), physical activity levels, and dietary habits all contribute to the body’s overall metabolic rate. The basal metabolic rate is the amount of energy expended while at rest, which is essential for maintaining vital bodily functions, such as breathing, circulation, and cellular production, even in the absence of food intake.
Moreover, metabolism is not a static process; it can vary between individuals due to genetic predispositions, muscle mass, age, and hormonal changes. As a result, two individuals consuming the same number of calories may experience different weight outcomes due to differences in metabolic rates. This highlights the importance of tailoring weight management approaches to an individual’s unique metabolic profile, rather than relying on general guidelines. In essence, a comprehensive understanding of metabolism and its components is critical when considering effective strategies for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. This foundational knowledge will pave the way for further exploration into the intricate relationship between metabolism, diet, and physical activity.
The Role of Metabolism in Weight Gain and Loss
Metabolism plays a crucial role in regulating body weight, acting as the biochemical engine that converts food into energy. It encompasses a series of chemical reactions that determine the rate at which calories are burned, significantly influencing weight management. At its core, metabolism is divided into two processes: anabolism, which builds up substances, and catabolism, which breaks them down. Both processes work together to maintain the body’s energy balance, a critical factor in weight gain or loss.
The metabolic rate, the speed at which the body expends energy, is influenced by several factors, including age, gender, muscle mass, and overall health. Individuals with a higher metabolic rate burn more calories at rest, thus playing a vital role in weight loss. For instance, muscle tissue requires more energy to maintain than fat tissue, meaning that people with greater muscle mass will have an enhanced metabolic rate. Conversely, a slower metabolism can lead to weight gain, as fewer calories are burned during daily activities.
Additionally, hormonal changes can significantly impact metabolic function. Hormones such as thyroid hormones, insulin, and cortisol can either speed up or slow down metabolism, affecting how food is processed and stored in the body. Lifestyle choices, including physical activity levels and dietary habits, also play a substantial role in determining metabolic rate. Incorporating regular exercise can help boost metabolism by building muscle mass and encouraging efficient calorie burning.
Ultimately, understanding that metabolism is not merely a function of genetic predispositions but can be influenced by lifestyle encourages a more holistic approach to weight management. By being aware of the factors affecting metabolism, individuals can take positive steps to achieve a healthier body composition. As such, incorporating healthy eating practices alongside regular physical activity can lead to improved metabolic health and support weight management efforts.
Factors Affecting Metabolic Rate
Metabolic rate is a crucial aspect of how efficiently the body converts food into energy, and several factors can significantly influence this rate. Understanding these factors can provide insights into why individuals experience differing metabolic rates and, consequently, variations in weight management.
Age is one of the primary determinants of metabolic rate. Generally, metabolism slows down as people age due to a natural decline in muscle mass and hormonal changes. Young adults typically have a faster metabolic rate compared to older adults, as their bodies are often more lean and muscular, which in turn increases energy expenditure.
Gender also plays a significant role in metabolic rates, with males usually exhibiting higher rates than females. This difference arises largely because men tend to have a higher muscle-to-fat ratio than women, resulting in increased basal metabolic rates (BMR). Hormonal variations further influence these disparities; for example, testosterone boosts muscle development, which can contribute to a higher metabolism.
Muscle mass is a critical factor as well, since muscles consume more energy than fat, even while at rest. Individuals with greater muscle mass often have elevated metabolic rates, making it easier for them to manage weight compared to those with lower muscle mass. Genetic predisposition also cannot be overlooked; hereditary factors may predispose certain individuals to be naturally inclined to have faster or slower metabolisms.
Lifestyle choices, including diet and physical activity levels, are essential for metabolic health. Regular exercise, particularly strength training, can enhance muscle mass and subsequently contribute to a more robust metabolic rate. Moreover, dietary habits play a crucial role; a balanced diet that promotes muscle retention can aid in sustaining a healthy metabolism over time.
Overall, understanding these various influences on metabolic rates equips individuals with the knowledge necessary to make informed lifestyle choices for effective weight management.
Why Metabolism Might Be Slow
Metabolism refers to the biochemical processes through which the body converts food into energy. A slow metabolism can significantly impact weight management, making it more challenging for individuals to maintain or lose weight. Various factors contribute to a sluggish metabolic rate, and understanding these can provide guidance for effective weight management strategies.
One common reason for slowed metabolism is hormonal imbalances. Hormones such as thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolic rates. For instance, individuals with hypothyroidism experience diminished hormone production, which can lead to reduced energy expenditure and a subsequent weight gain. Furthermore, hormonal fluctuations related to menopause or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also affect metabolism, causing it to slow down.
A sedentary lifestyle is another significant contributor to a reduced metabolic rate. Regular physical activity is essential not only for overall health but also for maintaining an active metabolism. When individuals leading a sedentary lifestyle engage in insufficient exercise, their muscles may lose mass over time. Since muscle tissue burns more calories than fat even at rest, a loss of muscle contributes to a slower metabolism, resulting in an energy deficit that can drive weight gain.
Diet also plays a vital role in metabolism. Poor nutritional choices, characterized by excessive calorie intake from processed foods and low nutrient density, can hinder metabolism. A diet lacking essential nutrients may leave the body without the necessary building blocks for optimal metabolic function. Additionally, chronic caloric restriction can signal the body to conserve energy, further slowing down the metabolic processes.
Specific health conditions, such as Cushing’s syndrome or certain medications, can adversely affect metabolism as well. Recognizing these factors can provide insights into weight management strategies that emphasize lifestyle modifications aimed at boosting metabolic rates.
The Impact of Diet on Metabolism
Diet plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, which is the process by which the body converts food into energy. The components of our diet, particularly macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, have distinct effects on metabolic rate. For instance, protein has a higher thermic effect compared to other macronutrients, meaning that consuming protein-rich foods can elevate metabolism more than carbohydrates or fats due to the energy required for digestion, absorption, and metabolism. This can be beneficial for weight management as it may promote a higher caloric expenditure.
Furthermore, incorporating foods rich in specific nutrients can also influence metabolic efficiency. For example, certain spices like cayenne pepper and ginger have been shown to potentially increase metabolic rates temporarily, while foods high in fiber can help regulate digestion and support a healthy metabolism. Staying hydrated is equally important; water is essential for all biochemical processes in the body, including those that involve metabolism. Studies indicate that drinking sufficient water can lead to a temporary increase in metabolic rate, a phenomenon often referred to as water-induced thermogenesis.
Meal timing is another crucial factor that affects metabolism. Research suggests that consuming regular meals and snacks can help maintain a consistently elevated metabolic rate throughout the day, whereas irregular eating patterns or prolonged fasting can slow down metabolic processes. Additionally, eating meals at strategic times—such as prior to physical activity—can enhance metabolic responses and improve fat oxidation. Understanding these dietary dynamics offers valuable insights for individuals aiming to manage their weight effectively. By making informed dietary choices, one can potentially maximize metabolic functioning, thus supporting their weight management efforts.
Exercise: A Catalyst for Metabolic Boost
Physical activity plays a crucial role in influencing metabolism, serving as a key catalyst that helps regulate metabolic processes essential for weight management. Engaging in regular exercise not only aids in burning calories but also assists in enhancing the body’s overall metabolic rate. As individuals develop a consistent exercise routine, they can effectively stimulate and sustain their metabolism, making it a vital component in the journey towards achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
One of the most effective forms of exercise for boosting metabolism is strength training. This type of physical activity focuses on building muscle mass, and as muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue, individuals can significantly increase their resting metabolic rate. Incorporating exercises such as weightlifting, resistance band exercises, and body-weight workouts can yield substantial results, especially when consistency is maintained over time.
Another highly beneficial approach is High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT), which alternates between short bursts of intense activity and periods of rest or lower intensity. This method not only maximizes calorie expenditure during workouts but also triggers a phenomenon known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), where the body continues to burn calories at an elevated rate even after the training session has concluded. Research suggests that HIIT can lead to substantial improvements in metabolic rates and promotes fat loss more effectively than traditional steady-state cardiovascular exercises.
In addition, incorporating a variety of physical activities into one’s routine can prevent monotony and stimulate different muscle groups. This not only maintains engagement but also promotes a well-rounded fitness regime that further aids in metabolic boosting. Therefore, making a commitment to regular movement through diverse forms of exercise, such as aerobics, cycling, or swimming, can significantly aid in optimizing metabolism and supporting successful weight management strategies.
The Role of Sleep and Stress in Metabolism
Metabolism, the process through which our bodies convert food into energy, is influenced significantly by external factors, particularly sleep and stress. Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining metabolic health, as it affects the hormones that regulate appetite and energy usage. When an individual experiences sleep deprivation, the body can react negatively. Studies have shown that lack of sleep can lead to an increase in ghrelin, the hunger hormone, and a decrease in leptin, the hormone responsible for signaling satiety. This hormonal imbalance often results in heightened appetite and cravings for high-calorie foods, ultimately contributing to weight gain.
Moreover, poor sleep can impair glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, crucial elements in weight management. Research indicates that chronic sleep deprivation may lead to poor dietary choices and reduced physical activity, compounding the risk of obesity and metabolic disorders. Thus, prioritizing sleep is vital for those seeking to manage their weight effectively.
On the other hand, chronic stress has its own detrimental effects on metabolism. When an individual is under prolonged stress, the body produces higher levels of the hormone cortisol. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased appetite and cravings, particularly for sugary and fatty foods. This phenomenon often results in a tendency to overeat and can exacerbate weight gain over time. Additionally, stress can alter the body’s energy expenditure and fat storage patterns, further complicating weight management strategies.
Therefore, cultivating habits for good sleep hygiene and managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness, regular physical activity, and adequate relaxation can significantly enhance metabolic health. By addressing these factors, individuals can improve not only their metabolic function but also their overall well-being, ensuring a more effective approach to weight management.
Tips to Stimulate Metabolism for Weight Loss
Enhancing metabolism is integral to effective weight loss, as it allows the body to efficiently convert nutrients into energy and maintain a healthy weight. Here are several strategies that can help stimulate your metabolic rate.
First and foremost, dietary adjustments play a critical role in metabolic function. Incorporating protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, legumes, and dairy products, can significantly boost metabolism. Studies suggest that the thermic effect of food, which involves the energy required for digestion, is higher for protein compared to carbohydrates and fats. Additionally, meals featuring whole foods and high fiber content can foster a feeling of fullness, reducing the overeating tendency.
Furthermore, engaging in regular exercise is essential for metabolic stimulation. Both aerobic and resistance training help burn calories and build muscle, which is metabolically active tissue. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has emerged as an effective method, providing significant metabolic benefits in a shorter duration compared to traditional workouts.
Hydration is another crucial factor. Drinking sufficient water can boost metabolic rates temporarily, particularly when consumed cold, as the body expends energy to heat the water to body temperature. Green tea and coffee, rich in antioxidants, may also enhance metabolism due to their caffeine content.
Prioritizing quality sleep is equally important. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased hunger and decreased metabolic rate. Developing a consistent sleep routine that promotes restorative rest can prevent these negative effects.
Lastly, managing stress is vital for maintaining metabolic health. Chronic stress leads to an increase in cortisol, which is associated with weight gain. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or simple breathing exercises can promote a balanced metabolic state.
By integrating these practices, individuals can significantly enhance their metabolism, facilitating more effective weight loss and improved overall well-being.
Conclusion: Embracing a Healthy Metabolism
In understanding metabolism, it is essential to recognize its critical role in weight management and overall health. Metabolism encompasses the complex biochemical processes that convert food into energy, influencing not only body weight but also the capacity to perform daily activities and maintain vitality. A well-functioning metabolism is vital, as it allows the body to efficiently utilize nutrients and manage energy expenditure.
The factors affecting metabolic rate range from genetic predisposition to lifestyle choices. For instance, age, gender, and muscle mass play significant roles in determining individual metabolic rates. However, lifestyle choices—including diet, physical activity, and sleep patterns—possess the power to enhance or impede the body’s metabolic efficiency. Consuming a balanced diet that includes whole foods, regular physical activity, and adequate hydration can significantly boost metabolic function, promoting effective weight management.
Furthermore, engaging in resistance training can help increase lean muscle mass, which in turn raises the resting metabolic rate. Similarly, incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into exercise routines has been shown to elevate metabolism post-workout, providing lasting benefits beyond the exercise session itself. Additionally, ensuring sufficient sleep and managing stress levels are crucial components in maintaining a healthy metabolic balance.
Ultimately, it is imperative to acknowledge that while certain aspects of metabolism may be beyond individual control, several lifestyle adjustments can lead to a healthier metabolic state. By adopting informed dietary choices, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining adequate rest, individuals can harness the power of metabolism to support their weight management journey. This holistic approach fosters not only a healthy body weight but also overall well-being, allowing individuals to lead more energetic and fulfilling lives.
Are you a coffee drinker? We all know caffeine can give a ‘kick-start’ to our day, but one noted health professional has gone a step further to create a unique method for turning coffee into a super-booster for your metabolism. Watch the video (link below) where he explains how this works and why, if you’re struggling to lose weight and your metabolism might be at fault, it might be of interest:
Watch Now: This Morning Coffee Tweak Could Be The Answer
Transparency Statement: Links featured on SLIMMRZ.com may take you to partner sites to which we are affiliated and as such should you choose to purchase anything from them we may receive a payment. This is how we afford to run and develop SLIMMRZ.com and in no way affects the amount that you pay. But please note that, although we have carefully reviewed them all, we can take no responsibility for the content of other sites and/or pages outside of this website and encourage you to do your own due diligence and listen carefully, or read fully, the content of any external websites that you may visit before making any purchase.